Multiplying or Dividing Both Sides of the Equation
Sometimes when solving equations, we may encounter variables with coefficients, which we need to remove to isolate the variable and find its value.
Exactly for those cases, and many more, we have the ability to multiply or divide both sides of the equation by the same number to maintain balance and solve for the variable.
With this method, we can multiply or divide both sides of the equation by the same element without thereby altering the overall value of the equation. This means that the final result of the equation will not be affected because we have multiplied or divided both sides by the same element or number.
In order to so we need to follow these two steps:
- Identify the Coefficient: Determine if multiplication or division is needed to isolate the variable.
- Apply Operation to Both Sides: Multiply or divide by the coefficient’s reciprocal.
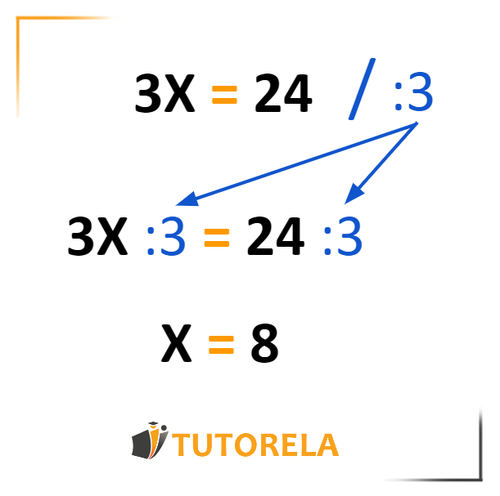
It's important to remember that when we multiply or divide both sides of an equation, the equation's balance should remain unchanged. This means we can always reverse the operation to return to the original equation. If reversing leads to a different result, it indicates that an error was made in the calculations.









