Equation A
3a=9
Equation B:
a+2=5
Equation C:
93a=1
Let's solve the three equations:
Equation A:
3a=9
Let's divide the equation by 3:
a=3
Equation B:
a+2=5
Subtract 2 from both sides of the equation:
a+2−2=5−2
a=3
Equation C:
93a=1
Simplifying the fraction 93 we obtain the following
3a=1
Now we multiply by 3 both sides of the equation
3a×3=1×3
a=3
Even if you haven't understood how we solved each of the equations don't worry, it's okay, later on, you will learn how to solve equations of this type easily. Our goal in this class is the solution of the equations. Notice that, for each of the three equations we have obtained the same solution, that is, a=3. Try to place this solution in each one and verify that it is correct.
These three equations are equivalent equations since they have the same unknown and the same solution.
Keep in mind that you can go from any equation to an equivalent one through some simple algebraic operations.
For example, let's look at the equation:
2z=8
By solving this equation we will obtain
z=8 :2
z=4
Now let's return to the original equation.
2z=8
Let's create an equivalent equation based on it, for example, by multiplying
2z=8 /×3
6z=24
This equation is equivalent to our original one. You can verify it by placing the obtained solution in the original equation z=4
6×4=24
24=24
That is, this is really the solution.
We can go from any equation to its equivalent equation through algebraic operations, just as we went from the original to the equivalent with a multiplication in this last example.
Note: Keep in mind that every equation has infinite equivalent equations since we can always create others with the algebraic operations we want.
3X−9=5
9X−27=15
6X−10=2X+7
24X−40=8X+28
Equation composed of two algebraic expressions with a = sign between them,
2x=10
This is an example of an equation. The algebraic expression placed on the right side is called the "right-hand side" and the one on the left is called the "left-hand side". The letters that appear in the equation, such as the letter x are called variables. The solution of the equation is a number that, if placed in place of the variable, will yield a correct answer. For example, in the previous equation, if we place the number 5 in place of the X we will get a correct answer.
2×5=10
10=10
The sides of the equation are equivalent, that is, the answer is correct.
What are equivalent equations?
Equation A:
2x=10
Equation B:
x+1=6
Let's solve equation A
2x=10
Divide by 2:
x=5
Now let's solve equation B
x+1=6
Subtract 1 from both sides of the equation
x=5
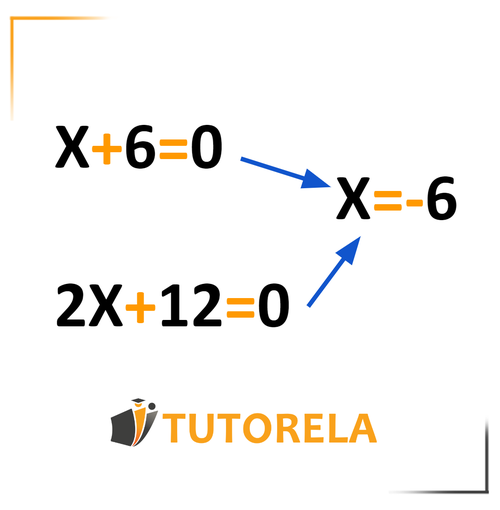
We found that the correct solution for both equations is x=5, which implies that these equations are equivalent - they have the same unknown and the same solution.
What is an equivalent in mathematics?
To understand what an equivalent equation is, let's first define what an equivalent in mathematics is. The concept of equivalent refers to a mathematical expression equal to another, that is, it represents the same quantity that may be written differently.
What are equivalent equations?
These are equal equations, that is, equations that represent the same thing, equations that have the same solution, in addition to having the same variable as unknown.
How to know if one function is equivalent to another?
To determine if one function is equivalent to another, the solution must be found in both functions and verify that the two equations are of equal value, let's see with an example.
Example
Task. Determine if the following equations are equivalent
Equation 1.
2x+5=7
Equation 2.
8x+20=28
Solution:
Let's find the solution of equation 1, by isolating x on one side of the equal sign, that is, leaving the variable x alone on one side of the equal sign.
2x=7−5
2x=2
x=22
x=1
The solution to equation 1 is x=1
Now let's find the solution of equation 2 in the same way
8x+20=28
8x=28−20
8x=8
x=88
x=1
We can observe that the second equation also has x=1 as its solution. Therefore, we conclude that the equations are indeed equivalent equations.
Answer
Yes, they are equivalent equations.