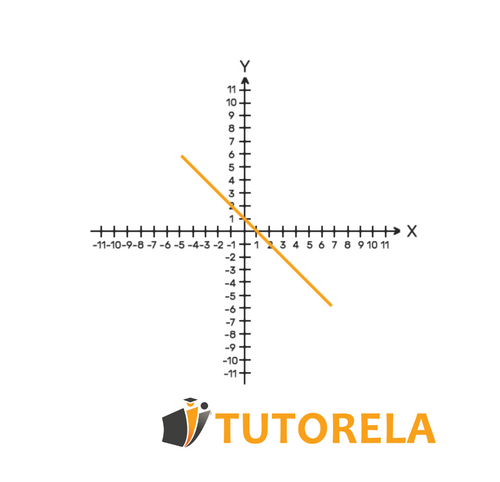
Decreasing function
What is a Decreasing Function?
A decreasing function is a type of relationship where, as you move to the right on the graph (increasing the xxx-value), the -value gets smaller. It’s like going downhill—the farther you go (the more you increase ), the lower your height (the -value) becomes.
We will say that a function is decreasing when, as the value of the independent variable increases, the value of the function decreases.
How to Spot a Decreasing Function:
- On a Graph: The line or curve goes downward as you move from left to right.
- In Numbers: For any two -values, if the second number is larger than the first \(x_2 > x_1\), then the second -value will be smaller than the first .
Real-Life Example:
Think about eating a stack of cookies. Every time you eat one, the number of cookies left in the stack gets smaller. That’s a decreasing function—your -value (cookies left) decreases as your -value (number of cookies eaten) increases.
Fun Fact:
If the line or curve always goes down without stopping, it's called strictly decreasing. If it flattens for a bit before going down again, it’s just decreasing.
Let's see an example of strictly decreasing linear function on a graph: