A polygon defines a geometric shape that is made up of sides. In other words, under the umbrella of polygons fall the following square, rectangle, parallelogram, trapezoid, and many more.
Area of Rectangle Practice Problems and Polygon Areas
Master rectangle area calculations and polygon area problems with step-by-step practice. Learn formulas, solve complex shapes, and build confidence in geometry.
- Calculate rectangle areas using the width × length formula
- Solve complex polygon area problems by dividing shapes into rectangles
- Apply the completion method to find areas of irregular polygons
- Master triangle, parallelogram, and trapezoid area calculations
- Combine multiple polygon areas to solve composite shape problems
- Use proper units and measurements in area calculations
Understanding Areas of Polygons for 7th Grade
Areas of Polygons
Polygon Definition
For example, a triangle has 3 sides, every quadrilateral has 4 sides, and so on.
We have already learned to calculate the areas of standard polygons. There are also non-standard polygons, for which there is no specific formula. However, their area of complex shapes can be calculated using two methods:
- We can divide the area of the required polygon into several areas of polygons that we are familiar with, calculate the areas separately, and then add them together to obtain the final area.
- We can try to "complete" the area of the required polygon into another polygon whose area we know how to calculate, and the proceed to subtract the area we added. This way, we can obtain the area of the original polygon.
Example
Let's demonstrate this using a simple exercise:
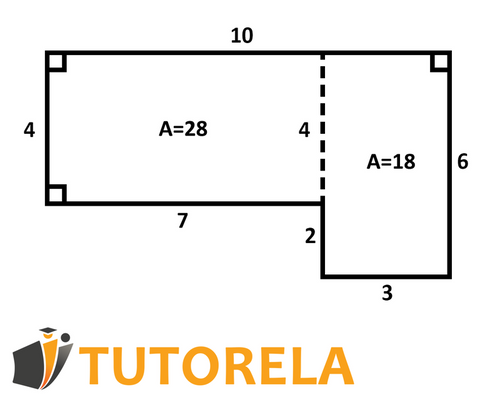
Here is a drawing of a polygon.
We need to calculate its area. From the start, we can see that this is not a standard polygon, so we will use the first method to calculate its area. We will divide the polygon as shown in the drawing, and we should obtain two rectangles.
According to the data shown in the drawing, in the rectangle on the right side we obtain the side lengths of 3 and 6, therefore the area of the rectangle will be 18 (multiplication of the two values). In the rectangle on the left side we obtain the side lengths of 4 and 7, therefore the area of the rectangle will be 28 (multiplication of the two values). Thus, the total area of the polygon will be the sum of the two areas we calculated separately, meaning, 18+28=46.
Practice Areas of Polygons for 7th Grade
Look at the rectangle ABCD below.
Given in cm:
AB = 10
BC = 5
Calculate the area of the rectangle.
Examples with solutions for Areas of Polygons for 7th Grade
Calculate the area of the right triangle below:
Due to the fact that AB is perpendicular to BC and forms a 90-degree angle,
it can be argued that AB is the height of the triangle.
Hence we can calculate the area as follows:
Answer:
24 cm²
Calculate the area of the triangle ABC using the data in the figure.
First, let's remember the formula for the area of a triangle:
(the side * the height that descends to the side) /2
In the question, we have three pieces of data, but one of them is redundant!
We only have one height, the line that forms a 90-degree angle - AD,
The side to which the height descends is CB,
Therefore, we can use them in our calculation:
Answer:
36 cm²
The trapezoid ABCD is shown below.
AB = 2.5 cm
DC = 4 cm
Height (h) = 6 cm
Calculate the area of the trapezoid.
First, let's remind ourselves of the formula for the area of a trapezoid:
We substitute the given values into the formula:
(2.5+4)*6 =
6.5*6=
39/2 =
19.5
Answer:
The trapezoid ABCD is shown below.
Base AB = 6 cm
Base DC = 10 cm
Height (h) = 5 cm
Calculate the area of the trapezoid.
First, we need to remind ourselves of how to work out the area of a trapezoid:
Now let's substitute the given data into the formula:
(10+6)*5 =
2
Let's start with the upper part of the equation:
16*5 = 80
80/2 = 40
Answer:
40 cm²
What is the area of the triangle in the drawing?
First, we will identify the data points we need to be able to find the area of the triangle.
the formula for the area of the triangle: height*opposite side / 2
Since it is a right triangle, we know that the straight sides are actually also the heights between each other, that is, the side that measures 5 and the side that measures 7.
We multiply the legs and divide by 2
Answer:
17.5