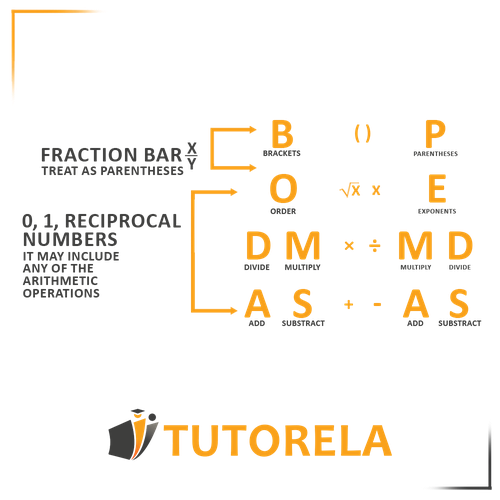
The order of mathematical operations with fractions is no different from the order of operations without fractions.
This means that if you know how to correctly solve a certain exercise based on the order of mathematical operations, you will also know how to solve an exercise with fractions in the same way.
Let's remember the order of operations:
- Parentheses - We always start by solving what is inside the parentheses, regardless of the type of operation it is.
- Multiplications and divisions – The exercise is read from left to right. Multiplications and divisions have the same hierarchy, therefore, we will resolve them according to their order of appearance in the exercise, from left to right.
- Additions and subtractions - After having solved the operations that were in parentheses and those of multiplying and dividing, we will continue with addition and subtraction.
They also share the same hierarchy, therefore, we will resolve them according to their order of appearance in the exercise, from left to right.
Note - We have not given any importance to fractions, nor have we mentioned them.
We will treat fractions like any other number, whether it is a common fraction or a decimal number, it's all the same.
3+6×31=
Solution:
Multiplication comes before addition, therefore, we will first solve all the multiplications.
We will obtain:
3+36
Now we will add and get:
3+2=5
52×(1+3)+4=
Solution:
Parentheses come first, so we will start by solving what's inside them.
We will obtain:
52×4+4=
Multiplication comes before addition, so we will continue with the multiplication.
We will obtain:
58+4
Now we will add and get:
458=553
0.3+(0.4+0.1)×4=
Solution:
We will start with the expression inside the parentheses.
We will solve and obtain:
0.3+0.5×4=
Multiplication is resolved before addition, so we will continue with it.
We will obtain:
0.3+2=
We will add and get:
0.3+2=2.3
8−9:18×6+5=
Solution:
We know that if there are no parentheses we start with multiplication and division.
But in what order?
According to the order of appearance in the exercise, from left to right.
We start reading the exercise and we come across a division, therefore, we will start with it.
We will obtain:
8−189×6+5=
We will continue with the multiplication. We will realize that 189 is, in fact, 21
We will obtain:
8−21×6+5=
8−3+5=
Now we will continue with the addition and subtraction operations according to the order of appearance.
When we start reading the exercise from the beginning we come across a subtraction, therefore, we will resolve it first. We will obtain:
5+5=10
5×3−84×2−3=
Solution:
There are no parentheses, so we will start with the multiplication and division operations according to their order of appearance in the exercise.
We will start with the first multiplication on the left.
We will obtain:
15−84×2−3=
We will continue with the next multiplication and obtain:
15−88−3=
We will realize that 88 is 1.
We will subtract from left to right according to the order of appearance and obtain:
15−1−3=
14−3=11