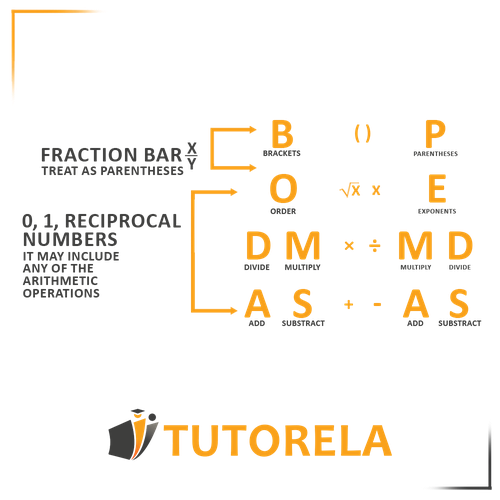
Fractions do not influence the order of operations, therefore, you should treat them like any other number in the exercise.
The correct order of mathematical operations is as follows:
- Parentheses
- Multiplications and divisions in the order they appear in the exercise
- Additions and subtractions in the order they appear in the exercise