As we have already learned, Coordinate System has two axes and, therefore, any value defined by this coordinate system must include two values. These two values are called "ordered pairs".
Ordered pair
What is an ordered pair?
An ordered pair is a pair of numbers that "belong" to a function.
An ordered pair is generally represented in parentheses where the value on the left within the parentheses represents the solution, while the value on the right within the parentheses represents the function value, that is, the result.
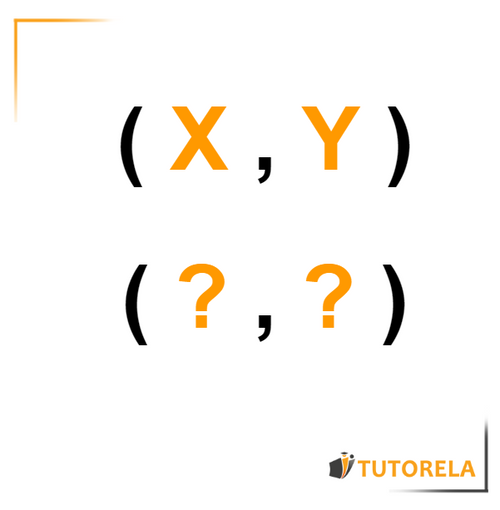
- When the function is represented by an equation, then is the value placed in the equation, while is the result obtained.
- When the function is represented through a graph, each point on the graph is essentially an ordered pair. That is, if we move vertically from the point to the axis (the axis runs from left to right), we obtain the value on the left within the parentheses. Conversely, if we move from the point vertically to the axis (the axis that goes from bottom to top), we obtain the correct value within the parentheses.
An ordered pair represents virtually all the points on the function graph
Test yourself on ordered pair!
Which point is marked on the graph?
Let's consider two examples of an ordered pair
Example 1
Given the equation:
- is the independent variable, meaning, the value that we input into the equation.
- is the dependent variable, meaning, the result obtained after deciphering the value of .
- If we establish that, we obtain that , that is, a point or the ordered pair is on the linear function .
- If we establish that , we obtain that , that is, a point or the ordered pair is on the linear function.
- If we establish that , we obtain that , that is, a point or the ordered pair is on the linear function .
Example 2
Given the equation represented by the following graph:
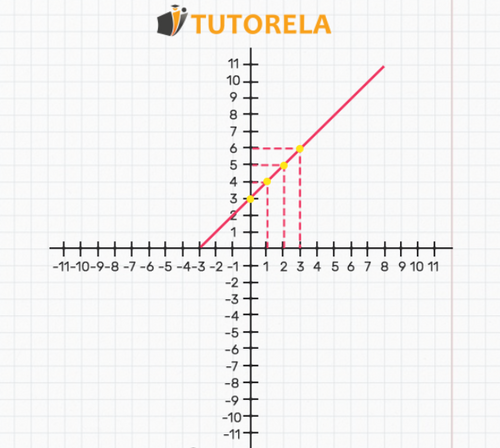
These ordered pairs are represented not only in a calculable manner, but also in the graph.
Any point on the graph of the function can be represented by an ordered type of values that can be easily found by drawing two verticals to each of the coordinates. These verticals are represented in the graph by dashed lines. If any point is on one of the axes, it means that the value of the other axis is zero, as in the case of in the present example.
If you are interested in more information about "graphs" you can find detailed information in the following articles:
Data collection and organization - statistical research
Reading information from graphs
On the Tutorela website, you will find a variety of articles with interesting explanations about mathematics
Examples and exercises with solutions of ordered pairs
Exercise #1
Which point is marked on the graph?
Video Solution
Answer
Exercise #2
Which point is marked on the map?
Video Solution
Answer
Exercise #3
Choose the appropriate drawing where the dots appear:
Video Solution
Answer
Exercise #4
Choose the appropriate drawing where the dots appear:
Video Solution
Answer
Exercise #5
Choose the appropriate drawing where the dots appear:
Video Solution
Answer
Which point is marked on the graph?
Which point is marked on the map?
Choose the appropriate drawing where the dots appear:
\( (-5,1),\lparen7,0),(-4,-1) \)
- Inequalities
- Graphs
- Reading Graphs
- Value Table
- Discrete graph
- Continuous Graph
- Numerical Value
- Function
- Linear Function
- Graphs of Direct Proportionality Functions
- Slope in the Function y=mx
- The Linear Function y=mx+b
- Finding a Linear Equation
- Positive and Negativity of a Linear Function
- Representation of Phenomena Using Linear Functions









