The addition and subtraction of real numbers are based on certain key principles. All principles will be explained using two real numbers, but certainly, the numbers in the exercise do not influence the method of resolution, therefore, these principles can be applied to any number in the exercise.
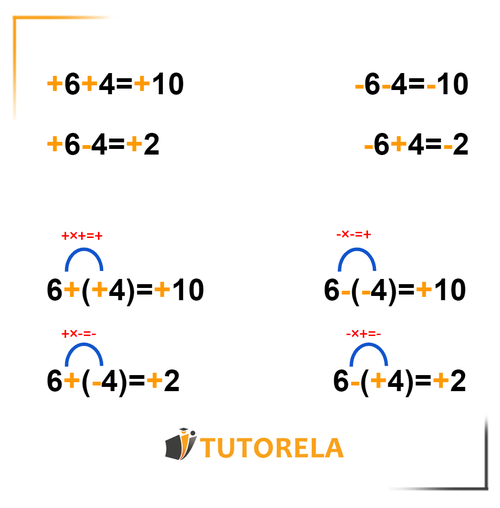
- When we have two real numbers with the same sign (plus or minus), this sign will remain in the result, which will, in fact, be the result of the addition. That is, if both numbers have a plus sign the result of the addition will also be positive. If both numbers have a minus sign the result of the subtraction will also be negative.
- When we have two numbers with different signs it is crucial to determine which of the two has the greater absolute value (absolute: the distance from zero). The larger number will determine the sign of the result and, in fact, we will perform a subtraction operation.
- When we have an exercise with a sequence of two signs (usually separated by parentheses) we will differentiate between several cases:
- When the sequence is of two plus signs the result will also be positive
- When the sequence is of two minus signs the result will also be positive
- When the sequence is of minus and plus or of plus and minus the result will be negative.