The Pythagorean Theorem can be formulated as follows: in a right triangle, the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the legs.
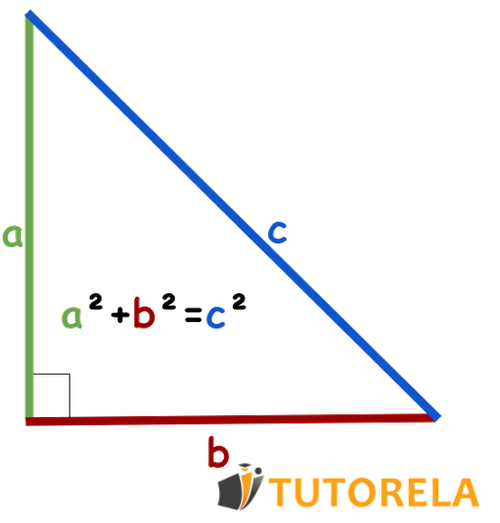
In the right triangle shown in the image below, we use the first letters of the alphabet to indicate its sides:
and are the legs.
is the hypotenuse.
Using these, we can express the Pythagorean theorem in an algebraic form as follows:
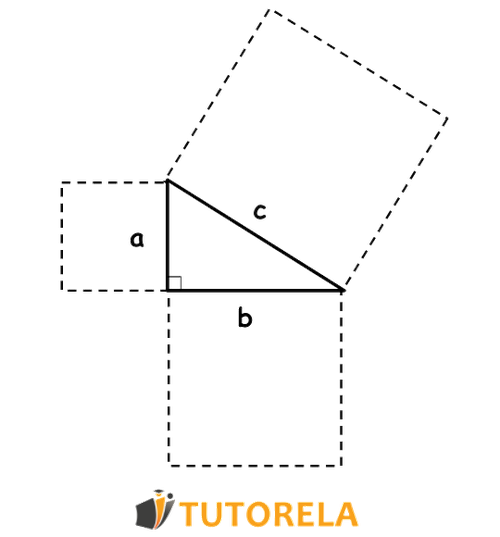
We can express the Pythagorean Theorem in a geometric form in the following way, showing that the area of the square () (square of the hypotenuse) is the sum of the areas of the squares () and () (squares of the legs).