
In a kite - the main diagonal - axis of symmetry:
• Bisects the vertex angles.
• Serves as a median to the secondary diagonal - divides it into two equal parts.
• Serves as a height to the secondary diagonal - creates a 90-degree angle with it.

In a kite - the main diagonal - axis of symmetry:
• Bisects the vertex angles.
• Serves as a median to the secondary diagonal - divides it into two equal parts.
• Serves as a height to the secondary diagonal - creates a 90-degree angle with it.
First, let's recall what a kite is:
A kite is composed of two isosceles triangles with a shared and identical base. Let's see this in an illustration:

is the common base - also called the secondary diagonal
is the main diagonal - also called the axis of symmetry
Vertex and vertex are both main vertices
Vertex and vertex are both base vertices

The axis of symmetry in a kite is the line connecting the two vertices of the head and is also called the main diagonal.
The line is called the axis of symmetry because it divides the kite symmetrically and perfectly into two equal parts.
Serves as a height to the common base so that angle and angle and angle and angle are all equal to degrees each.
And
Serves as a median to the common base so that: equals
And
Serves as a vertex angle bisector so that:
Angle equals angle
And angle equals angle
Angle equals angle
So if we combine all the properties we've gathered here together, we can summarize that:
In a kite, the axis of symmetry - the main diagonal is also the bisector of the vertex angles, is perpendicular to the secondary diagonal forming a 90-degree angle, and bisects it.
To summarize, the properties of a kite are:
An axis of symmetry is essentially a line where if you fold the shape in half along this line, the parts align perfectly and identically.
You can cut out a kite on paper, draw a line that would be the main diagonal - the axis of symmetry, and see how the parts of the kite merge precisely with each other.
The term "axis of symmetry" will help you remember that the main diagonal divides both the angle, the secondary base, and creates a right angle.
And now that you deeply understand what an axis of symmetry is and how it affects the properties of a kite, it's time to practice! Ready?
Exercise:
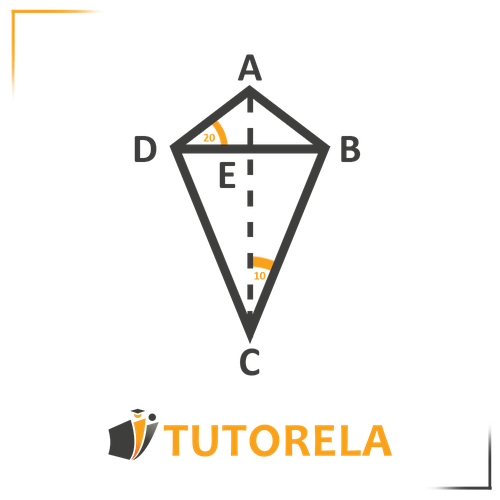
Here is a kite.
Given that:
Angle
Angle
Calculate all the angles in a kite.
Solution:
We know that a kite is composed of two isosceles triangles.
Meaning triangle is isosceles
and triangle is isosceles.
Therefore if angle then angle - base angles are equal in an isosceles triangle.
Therefore angle since the sum of angles in a triangle is .
From this we can also conclude that angles and are equal to each. The main diagonal bisects the vertex angle into two equal parts.
Let's continue to the bottom part of the kite:
Angle since the main diagonal bisects the vertex angle into two equal parts.
Now to find out what angles and equal
We'll look at the bottom isosceles triangle and understand that since the vertex angle equals , both angles need to sum up to and they are equal. Therefore:
Each of these angles equals .
Additional Exercise:
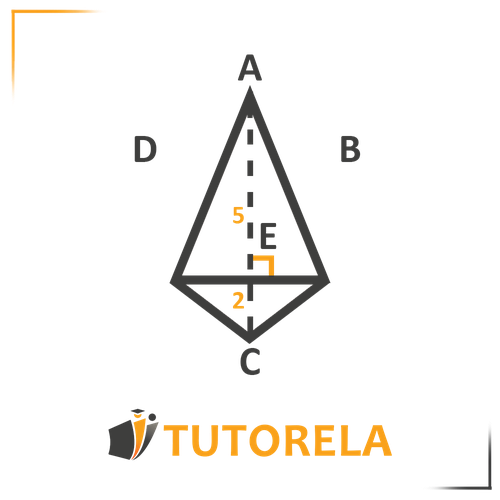
Given a kite ABCD
Given that:
AE= 5 DE=2
Find the length of AB
Solution:
Given a kite where and
Since the main diagonal is also a median to the secondary diagonal, we can conclude that .
Since the main diagonal is also perpendicular to the secondary diagonal, we can conclude that angle is a right angle, therefore triangle is a right triangle.
From here we can use the Pythagorean theorem and find that