To find out when the parabola is positive and when it is negative, we must plot its graph.
Then we will look at
When the graph of the parabola is above the axis, with a positive value, the set is positive
When the graph of the parabola is below the axis, with a negative value, the set is negative
Let's see it in an illustration:
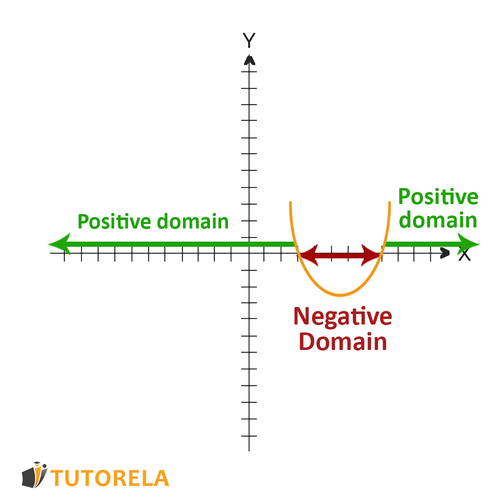
We will ask ourselves:
When is the graph of the parabola above the axis?
When or
Therefore, the sets of positivity of the function are: ,
Now we will ask When is the graph of the parabola below the axis?
When
Therefore, the set of negativity of the function is: