When a problem is presented to us in writing, we can convert it into mathematical language (also called algebraic language) by transforming it into an algebraic expression. But what are algebraic expressions?
Variable: This is a letter that represents a numerical value, for example or . This letter refers to an unknown numerical value that we must work out. For example: if , then we can conclude that the numerical value of is .
An algebraic expression is a combination of numbers and letters (representing unknown numbers) that includes operations such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, etc.
Each element of an algebraic expression is called an algebraic term, be it a variable, a constant, or a combination of a coefficient and one or more variables. If the expression contains only one term, it is known as a monomial, while those that contain two or more terms are polynomials.
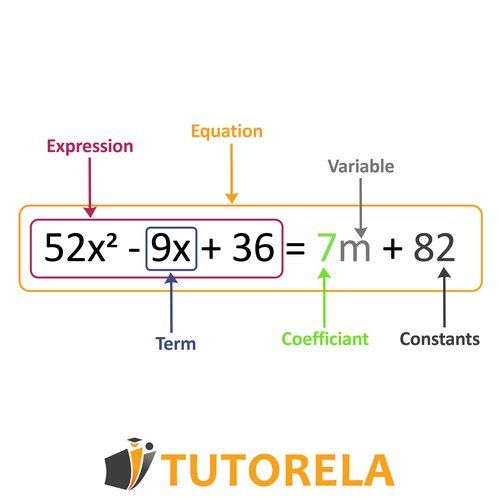
There is no limitation to the amount of constant numbers, unknown variables, or operations that can appear in an algebraic expression. In addition, there does not always have to be a variable in the algebraic expression, although it will always have a certain numerical value.