Understanding Sides, Vertices, and Angles in Geometry
In geometry, shapes are defined by three key components: sides, vertices, and angles. These elements work together to form polygons and other figures, helping us understand their properties and relationships.
The number of sides in a polygon equals the number of vertices and angles. For example, a hexagon has six sides, six vertices, and six angles.
Definitions:
Side
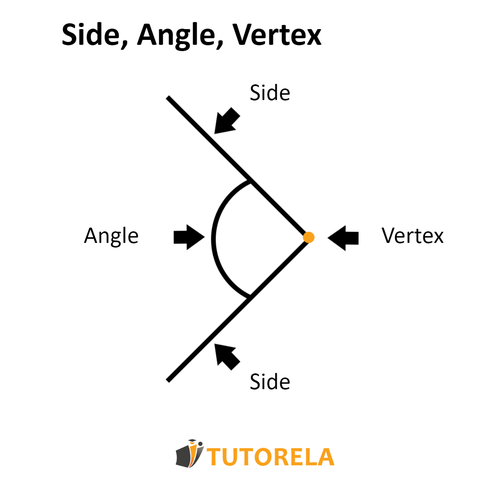
A side is the straight line that lies between two points called vertices. An angle is formed between two lines. Sides form the edges of a polygon. For example, a triangle has three sides, while a square has four. The length and arrangement of sides determine the size and shape of a figure.
Vertex
A vertex is the point of origin where two or more straight lines meet, thus creating an angle. These vertices are often referred to as the "corners" of a shape. A triangle has three vertices, a square has four, and a pentagon has five.
Angle
An angle is created when two lines originate from the same vertex. The measure of an angle indicates the degree of rotation between the two sides. Angles can be acute (less than ), right (), obtuse (greater than ), or straight ().
To clearly illustrate these concepts, we will represent them in the following drawing: