Every triangle consists of sides and the sum of angles in every triangle is degrees.
Parts of a Triangle
Triangle Components
In an equilateral triangle -
• All the sides are equal
• All the angles are equal and each angle equals degrees
• Every height is also a median and an angle bisector.
In an isosceles triangle -
• The two legs are equal
• The two base angles are equal
• The median from the vertex angle is also the height to the base and the vertex angle bisector.
In a right triangle -
• There is one angle of degrees formed by two legs
• The side opposite to the right angle is called the hypotenuse.
In a scalene triangle -
• All sides in the triangle are different from each other
• All angles in the triangle are different from each other.
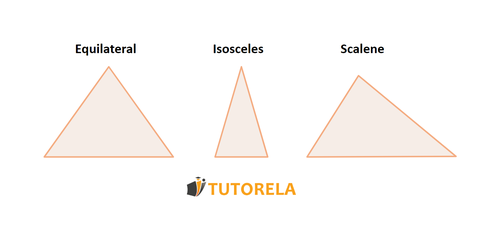
Triangle Components
Triangle components - what is a triangle made of?
A triangle is a shape made up of sides and the sum of its angles is always equal to .

We can see that three sides do make up the triangle, as we counted in the illustration.
We can also conclude that: since we know that the sum of angles in a triangle is degrees.
Important to know – these properties characterize all types of triangles.
Types of Triangles
Now we will focus on the different types of triangles and understand what they consist of:
Equilateral Triangle -
If all three sides are equal - it is an equilateral triangle. An equilateral triangle is a triangle where:
- All sides are equal
- All angles are equal and each equals degrees
- Every height is also a median and an angle bisector.
Let's look at an illustration:
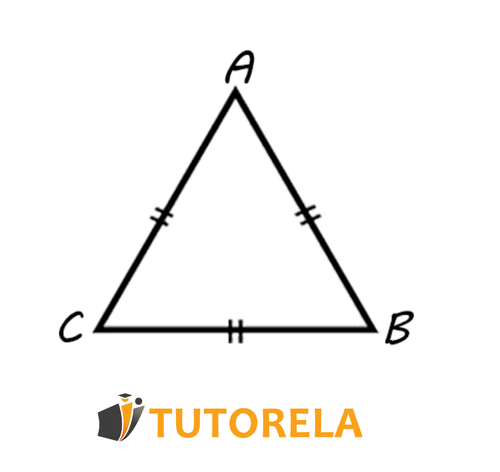
In an equilateral triangle, all sides are equal (as its name suggests - equilateral triangle) and all angles are equal.
Since we learned that the sum of angles in any triangle is , we can deduce that each angle equals .
Additionally, every height is also a median and an angle bisector, so it doesn't matter from which angle we draw a height, it will serve as both an angle bisector and a median to the side it reaches.
Click here to learn more about equilateral triangles
Isosceles triangle
If only two sides are equal - it is an isosceles triangle. The two equal sides are called legs and the third side is called the base.
An isosceles triangle is a triangle in which:
- The two legs are equal
- The two base angles are equal
- The median from the vertex angle is also the height to the base and also bisects the vertex angle.
Let's look at an illustration:
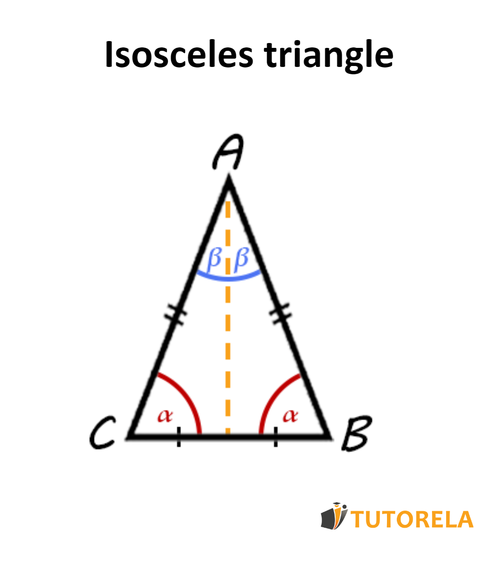
In the illustration, we can see that the two legs of the triangle are equal (hence its name - isosceles), and the two base angles are equal.
The height to the base that extends from the vertex angle also serves as the median to the base (divides it into equal halves) and also serves as the angle bisector of the vertex angle.
You can read more about isosceles triangles at this link
Scalene triangle -
If each side is different from the other sides - it is a scalene triangle. A scalene triangle is a triangle where:
- All sides in the triangle are different from each other.
- All angles in the triangle are different from each other.
Let's look at an illustration:
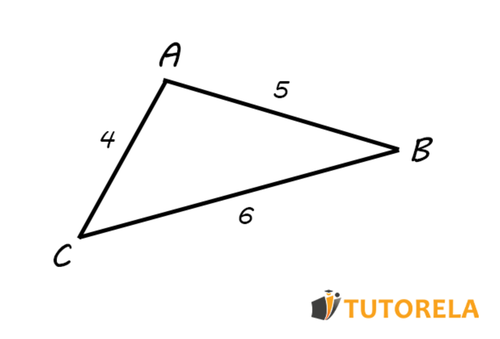
We observe that each side has a different length from the other sides. From this, we can also deduce that each angle is different in size from the other angles in the triangle.
In this link you can read in detail about scalene triangle
Right triangle -
A right triangle is a triangle in which:
- There is one angle of degrees formed by two legs.
- The side opposite to the right angle is called the hypotenuse.
Let's look at an illustration:
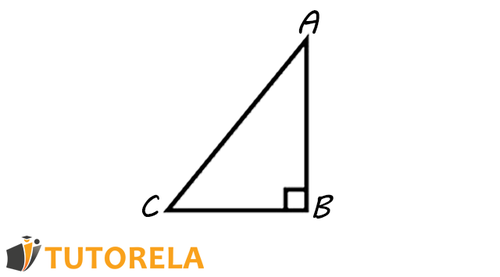
In the illustration, we can see that a right triangle consists of two sides that are perpendicular to each other - each such side is called a leg. These two sides form an angle of degrees between them.
We also learned that the side opposite to the right angle is called the hypotenuse - that's the only one left.
To learn more about right triangles - click here
Triangle Components
Height in a triangle
A height in a triangle is a straight line extending from a specific vertex to its opposite side, forming a degree angle.
The height can be inside or outside the triangle.
Example of heights inside a triangle:
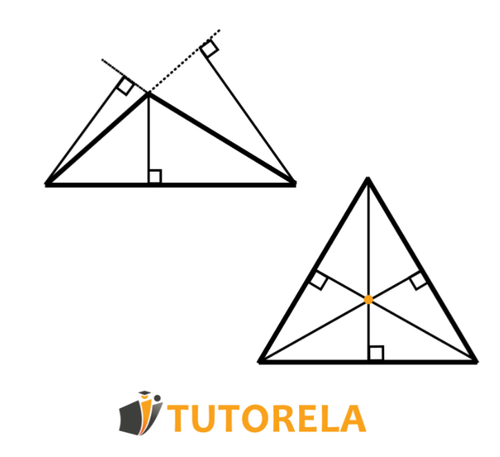
Every height extends from a certain vertex to the opposite side and creates a degree angle with it.
*Note: In a right triangle, the height is also the leg.

Example of a height outside the triangle:

Note - a height that is outside the triangle will always create a right angle with the extended imaginary side - the one that extends outside the triangle and not with the actual side of the triangle.
Angles in a Triangle
In any triangle, regardless of its type, the sum of angles is .
In an equilateral triangle - each angle equals degrees.
This means that if you have a triangle where two angles equal degrees, you can immediately conclude that the third angle also equals since it complements to degrees.
Additionally, you can conclude that the triangle is equilateral - meaning all sides are equal to each other.
In an isosceles triangle - the two base angles are equal and the third completes to .
This means that if you have a triangle with only two equal angles (whose size is different from ), the third angle will complete to .
Additionally, the sides opposite to the equal angles are called legs and the third side is called the base of the triangle.
The angle opposite to the base is called the vertex angle and the triangle is called isosceles.

In a right triangle - only one angle equals and the other two angles sum up to .
This means that if you have one angle equal to degrees, you can immediately determine that it is a right triangle.
The two sides forming the right angle will be called legs and the third side opposite to the right angle will be called the hypotenuse.
The triangle will be called a right triangle.
Bonus Note -
In a golden triangle - only one angle equals and the other two angles equal each, creating a triangle that is both isosceles and right-angled.
Angle bisector
An angle bisector is a line segment that extends from a certain side to the opposite vertex and divides the angle it meets into equal halves.
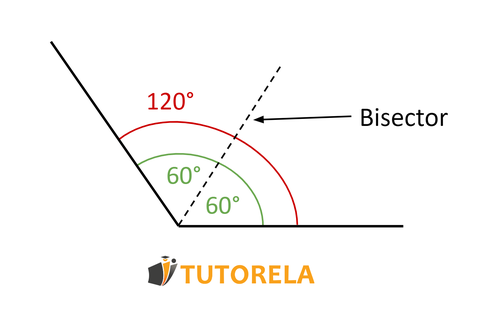
Bonus note: In an isosceles triangle, the angle bisector of the vertex angle is also the height to the base and the median.

There can be 3 angle bisectors in any triangle but each angle has only one angle bisector.
Click here to learn more about angle bisector
Center of the triangle
The center of the triangle, also called the intersection of medians, is a point inside the triangle where all the medians of the triangle meet.
There are main theorems you should know about:
- All three medians in a triangle intersect at a single point called the centroid.
This means that if two medians intersect at a point inside the triangle, the third median must also pass through it.
Additionally, if it is known that two medians intersect at a certain point and there is a straight line that passes through this point as well, it will be the third median in the triangle. - The intersection point of the medians - the centroid - divides each median in a ratio of where the larger part of the median is closer to the vertex.
This means that the longer part of the divided median is times larger than the shorter part of the divided median.

And now let's practice!
Question –
If the triangle consists of equal sides and another side that is not equal to them, determine which type of triangle it is.
Solution –
This is an isosceles triangle in which there are equal sides.
Another question -
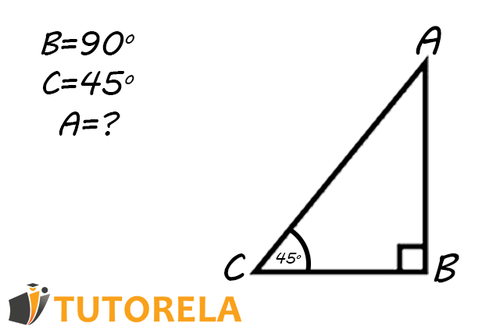
Given that in a certain triangle one angle equals and the second angle equals .
- What is the size of the third angle?
- What type of triangle is it?
Solution:
- We know that in every triangle the sum of angles is degrees.
If we add:
The third angle must complete to degrees, therefore it equals .
The size of the third angle is .
- This is a right triangle given that it has an angle equal to degrees.








