Every three-dimensional body has volume. For example, a ball or pyramid are bodies with volume. The volume of a body is our way of measuring the space that said body occupies in space.
For example, let's observe a cube whose length of each of its sides is , like this one:
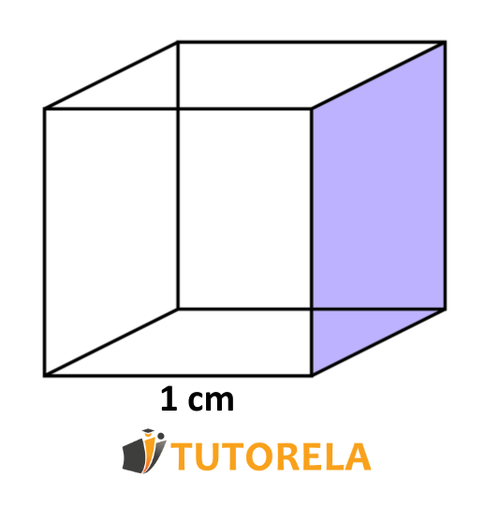
To calculate the volume of the cube we will use the known formula:
In this case, the three dimensions are equal and, therefore, we will note:
V is the letter used to abbreviate the word volume in exercises and is used to designate volumes.
That is, we found that the volume of the cube is cubic centimeter (cm raised to the third power)
Known volume measurement units:
Additionally, there are measurements that we primarily use for measuring liquids: